What Is Depression?
Depression, also known as major depressive disorder, is a medical condition characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities.
It is not a sign of weakness or something one can simply “snap out of.” Instead, it is a serious health condition that often requires professional intervention.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), depression is one of the leading causes of disability globally, affecting people of all ages, backgrounds, and walks of life.
Unlike occasional feelings of sadness that everyone experiences, depression is marked by its duration and intensity.
Symptoms typically persist for at least two weeks and can interfere with work, social interactions, and personal responsibilities. Understanding the signs of depression is the first step toward addressing it.

Depression: Symptoms, Causes & Management
Depression is a complex mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
It goes beyond temporary sadness or feeling “down” and can significantly impact daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
This article explores the symptoms, causes, and management strategies for depression, drawing on reputable sources to provide a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
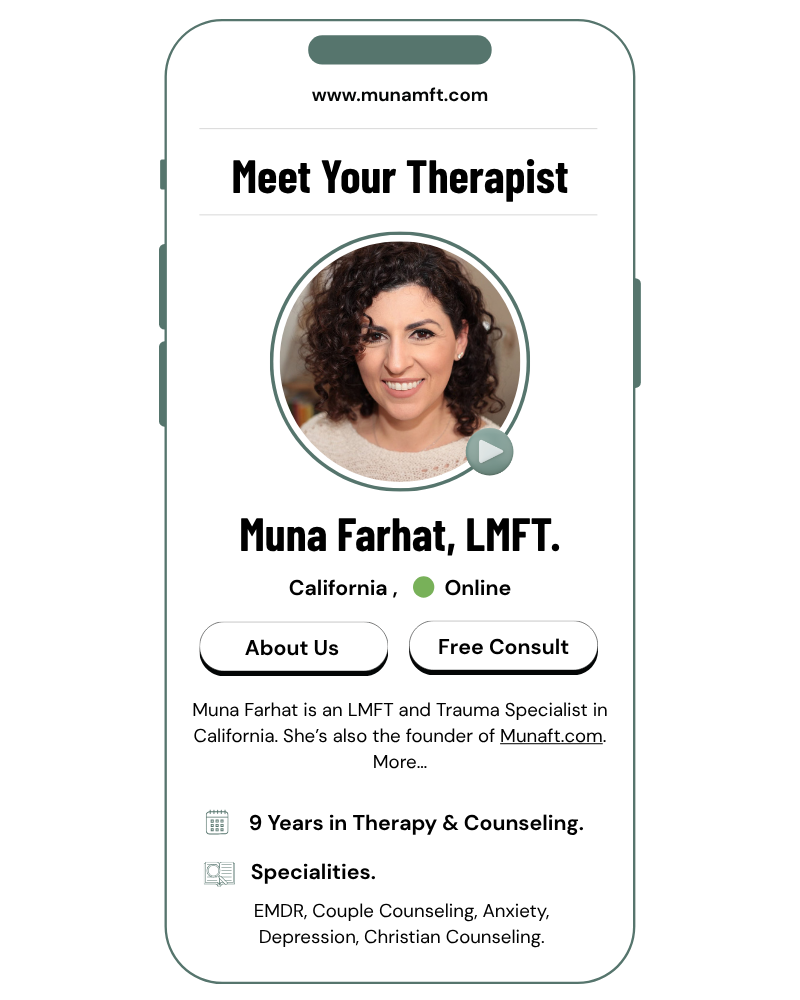
Book a free confidential consultation with Muna Farhat, the certified therapist in California.
Symptoms of Depression Symptoms
The symptoms of depression vary from person to person, but they often include a combination of emotional, physical, and cognitive changes. Below are some common signs, as outlined by the Cleveland Clinic and Mayo Clinic:
Emotional Symptoms:
- Persistent sadness, emptiness, or hopelessness.
- Feelings of guilt, worthlessness, or helplessness.
- Irritability or frustration, even over small matters.
- Loss of interest or pleasure in hobbies, social activities, or things once enjoyed.
Physical Symptoms:
- Changes in appetite, leading to weight loss or gain.
- Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or oversleeping.
- Fatigue or low energy, even after rest.
- Physical aches or pains without a clear cause, such as headaches or digestive issues.
Cognitive and Behavioral Symptoms:
- Difficulty concentrating, remembering, or making decisions.
- Slowed thinking, speaking, or body movements.
- Restlessness or trouble sitting still.
- Recurrent thoughts of death or suicide, or suicide attempts.
In some cases, depression may manifest differently depending on age, gender, or cultural background.
For example, children may show irritability or clinginess, while older adults might experience more physical complaints or memory issues. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early intervention.
Causes and Risk Factors
Depression is not caused by a single factor but rather results from a combination of biological, psychological, and environmental influences. Understanding these factors can help individuals and their loved ones better navigate the condition.
The WHO emphasizes that depression can affect anyone, regardless of socioeconomic status or personal circumstances.
However, certain groups, such as women, individuals with chronic illnesses, or those experiencing discrimination, may face a higher risk.
Biological Factors
Brain Chemistry:
Genetics:
Physical Health Conditions:
Psychological Factors
Personality Traits
Trauma or Stress
Environmental Factors
Social Isolation
Socioeconomic Challenges
Substance Use
Types of Depression
Depression is not a one-size-fits-all condition. Several distinct types exist, each with unique characteristics:
Characterized by severe symptoms that interfere with daily functioning, lasting at least two weeks.
A chronic, milder form of depression that lasts for two years or more.
Depression that occurs at specific times of the year, often during winter months with reduced sunlight.
Severe depression that occurs after childbirth, affecting both mothers and, in some cases, fathers.
Involves episodes of depression alternating with periods of mania or elevated mood.
Depression accompanied by hallucinations, delusions, or other psychotic symptoms.
Each type requires tailored approaches to management, highlighting the importance of accurate diagnosis by a healthcare professional.

Diagnosis & When to Seek Help
Diagnosing depression typically involves a thorough evaluation by a doctor or mental health specialist. This may include:
- A detailed medical and personal history to identify symptoms and potential triggers.
- A physical exam to rule out underlying health conditions, such as thyroid disorders, that can mimic depression.
- Psychological assessments or questionnaires to evaluate the severity and impact of symptoms.
The Mayo Clinic notes that depression is often underdiagnosed because people may feel ashamed or unaware that their symptoms indicate a treatable condition.
If you or someone you know experiences symptoms of depression for more than two weeks, it’s important to seek professional support. Immediate help is critical if thoughts of self-harm or suicide are present.
Management & Treatment Options
Depression is treatable, and most individuals experience significant improvement with the right approach. Treatment often involves a combination of therapies tailored to the individual’s needs.
Psychotherapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to depression.
- Interpersonal Therapy (IPT): Focuses on improving relationships and communication skills to address social triggers.
- Other Therapies: Approaches like mindfulness-based cognitive therapy or psychodynamic therapy may also be effective.
Medications
- Antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), can help balance brain chemistry. These medications often take weeks to show effects and may require adjustments.
- Other medications, like mood stabilizers or antipsychotics, may be used for specific types of depression, such as bipolar disorder or psychotic depression.
Lifestyle Changes
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as walking or yoga, can boost mood by increasing endorphins and reducing stress.
- Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a consistent sleep routine can help alleviate symptoms like fatigue and irritability.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall health and may positively impact mood.
- Social Support: ConnectingWITH friends, family, or support groups can reduce feelings of isolation.
Other Interventions:
- Light Therapy: Used for seasonal affective disorder, this involves exposure to bright light to mimic natural sunlight.
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT): In severe cases where other treatments fail, ECT may be considered. It involves controlled electrical stimulation to the brain under anesthesia.
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): A non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate brain areas involved in mood regulation.
Coping Strategies for Everyday Life
In addition to professional treatment, individuals can adopt coping strategies to manage depression in daily life:
- Set Realistic Goals: Break tasks into small, manageable steps to avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Practice Self-Compassion: Avoid self-criticism and acknowledge that recovery is a journey.
- Engage in Enjoyable Activities:Even if motivation is low, try engaging in hobbies or activities that once brought joy.
- Limit Stress: Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation.
- Avoid Isolation: Reach out to trusted friends or family members, even if it feels challenging.
Supporting Someone with Depression
If someone you care about is struggling with depression, your support can make a difference. Here are some ways to help:

The WHO highlights the importance of reducing stigma around mental health. Open conversations and empathy can create a supportive environment for those affected.
The Global Impact of Depression
Depression is a global health challenge, with significant social and economic consequences. The WHO estimates that over 280 million people worldwide live with depression, and it contributes to a substantial portion of the global burden of disease.
In severe cases, depression can lead to suicide, which claims hundreds of thousands of lives annually.
Efforts to address depression include increasing access to mental health services, raising awareness, and integrating mental health care into primary healthcare systems.
Community-based programs and peer support networks also play a vital role in supporting those affected.
Moving Forward
Depression is a multifaceted condition that requires understanding, compassion, and proactive management.
By recognizing its symptoms, understanding its causes, and exploring treatment options, individuals can take meaningful steps toward recovery.
Whether you’re experiencing depression yourself or supporting someone who is, know that help is available, and improvement is possible with time and effort.
This article provides a foundation for understanding depression, but it’s not a substitute for professional advice. If you or someone you know is struggling, reaching out to a healthcare provider or mental health professional is an important step toward healing.
By understanding anxiety disorders and exploring evidence-based treatments, individuals can take meaningful steps toward reducing their symptoms and regaining control over their lives.
From Start to Finish: Therapy & Counseling in 3 Steps
1.
Book a free initial consultation to share your concerns and explore how therapy can support your mental health goals.
2.
After understanding your needs, your therapist will design a personalized therapy plan, incorporating approaches like CBT or mindfulness to address your unique challenges.
3.
Begin your therapy sessions—available in-person or online—with flexible scheduling options, and let your therapist guide you toward growth and emotional well-being.

Our Experience
Keyword Ideas (anxiety therapist near me, anxiety and OCD therapist, online anxiety therapy California, social anxiety California, relationship anxiety therapist)
Have Questions? We’ve Answers for You.
Find answers to your questions about therapy, Muna’s services and specialization, Insurance, or privacy here.
Muna Farhat, LMFT is a Licensed Marriage and Family Therapist based in San Jose, CA.
She holds the necessary credentials to practice therapy in California, with expertise in supporting individuals, couples, and families through various emotional and relational challenges.
As a Licensed Marriage and Family Therapist, Muna adheres to strict confidentiality standards outlined by California state law and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Your personal information is securely stored and only shared with your explicit consent, except in legally mandated situations.
Therapy is a collaborative process where you work with a trained professional, like Muna, to address emotional, mental, or relational challenges. It can help you gain insight, develop coping strategies, and achieve personal growth or resolution of specific issues.
Counseling and therapy are often used interchangeably, but counseling typically focuses on specific issues or short-term goals (e.g., coping with a life transition), while therapy may involve deeper exploration of long-standing patterns. Muna offers both, depending on your needs.