Understanding and Managing Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health conditions, affecting millions of people worldwide.
These disorders involve excessive worry, fear, or nervousness that can interfere with daily life. This blog explores the nature of anxiety disorders, their symptoms, types, diagnosis, and evidence-based treatment options.


What Are Anxiety Disorders?
Anxiety disorders are characterized by persistent and intense feelings of fear or worry that go beyond typical stress.
Unlike occasional anxiety, which is a normal response to challenging situations, anxiety disorders can cause significant distress and impair a person’s ability to function at work, school, or in relationships.
These conditions often develop due to a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors.
Common Types of Anxiety Disorders
Several distinct anxiety disorders exist, each with unique features:
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD):
Involves chronic, excessive worry about various aspects of life, such as health, finances, or work, often without a specific trigger.
Panic Disorder:
Marked by sudden, intense episodes of fear (panic attacks) accompanied by physical symptoms like a racing heart, shortness of breath, or dizziness.
Social Anxiety Disorder
Intense fear of social situations or being judged by others, leading to avoidance of interactions.
Specific Phobias:
Extreme fear of a particular object or situation, such as heights, spiders, or flying, which can lead to avoidance behaviors.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD):
Involves recurring, intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) performed to reduce anxiety.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD):
Develops after exposure to a traumatic event, causing flashbacks, nightmares, or severe anxiety.
Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders
Symptoms vary depending on the type of anxiety disorder but often include both emotional and physical signs
These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may fluctuate over time. If they persist for six months or more and disrupt daily life, it may indicate an anxiety disorder.
- Emotional Symptoms: Excessive worry, irritability, restlessness, or a sense of impending doom.
- Physical Symptoms: Increased heart rate, sweating, trembling, fatigue, muscle tension, or sleep disturbances.
- Cognitive Symptoms: Difficulty concentrating, racing thoughts, or trouble making decisions.
Diagnosing Anxiety Disorders
Diagnosing an anxiety disorder typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. The process may include:
1- Medical History Review:
To rule out physical health conditions or medications that could contribute to anxiety symptoms.
2- Psychological Assessment
A mental health professional may use standardized questionnaires or interviews to evaluate the severity and nature of symptoms.
3- Diagnostic Criteria
Clinicians refer to guidelines like the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) to confirm a diagnosis based on specific criteria, such as the duration and impact of symptoms.
It’s important to distinguish anxiety disorders from temporary stress or other mental health conditions, as accurate diagnosis guides effective treatment.
Treatment Options for Anxiety Disorders
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, or talk therapy, is a cornerstone of anxiety treatment. Common approaches include:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that fuel anxiety. CBT is widely regarded as one of the most effective treatments for anxiety disorders.
Exposure Therapy
A form of CBT that gradually exposes individuals to feared situations or objects to reduce avoidance and fear responses.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
Encourages individuals to accept their anxiety while focusing on actions aligned with their values.
Medications
Medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms, particularly for severe cases. Common options include:
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Often the first-line treatment, these antidepressants help regulate brain chemicals linked to mood.
Benzodiazepines
Used for short-term relief of acute anxiety but carry a risk of dependence.
Buspirone
An anti-anxiety medication that may be used for GAD.
Beta-Blockers
Sometimes prescribed to manage physical symptoms, like rapid heartbeat, during anxiety-provoking situations.
Medication should always be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare provider, as side effects and risks vary.

Lifestyle and Self-Help Strategies
In addition to professional treatment, lifestyle changes and self-help techniques can support anxiety management:
Regular Exercise:
Physical activity, such as walking or yoga, can reduce stress and improve mood.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques:
Practices like meditation, deep breathing, or progressive muscle relaxation can calm the mind and body.
Healthy Sleep Habits:
Prioritizing consistent sleep schedules and a restful environment can reduce anxiety symptoms.
Balanced Diet:
Limiting caffeine and alcohol, which can exacerbate anxiety, and eating nutrient-rich foods can support mental health.
Social Support:
Connecting with trusted friends, family, or support groups can provide emotional relief.
When to Seek Help
If anxiety symptoms interfere with daily activities, relationships, or overall well-being, it’s important to consult a healthcare or mental health professional. Early intervention can prevent symptoms from worsening and improve quality of life.
Living with Anxiety Disorders
Managing an anxiety disorder is an ongoing process, but with the right tools and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Treatment plans should be personalized, as what works for one person may not work for another. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider can help adjust strategies as needed.
By understanding anxiety disorders and exploring evidence-based treatments, individuals can take meaningful steps toward reducing their symptoms and regaining control over their lives.
From Start to Finish: Therapy & Counseling in 3 Steps
1.
Book a free initial consultation to share your concerns and explore how therapy can support your mental health goals.
2.
After understanding your needs, your therapist will design a personalized therapy plan, incorporating approaches like CBT or mindfulness to address your unique challenges.
3.
Begin your therapy sessions—available in-person or online—with flexible scheduling options, and let your therapist guide you toward growth and emotional well-being.

Our Experience
Keyword Ideas (anxiety therapist near me, anxiety and OCD therapist, online anxiety therapy California, social anxiety California, relationship anxiety therapist)
Have Questions? We’ve Answers for You.
Find answers to your questions about therapy, Muna’s services and specialization, Insurance, or privacy here.
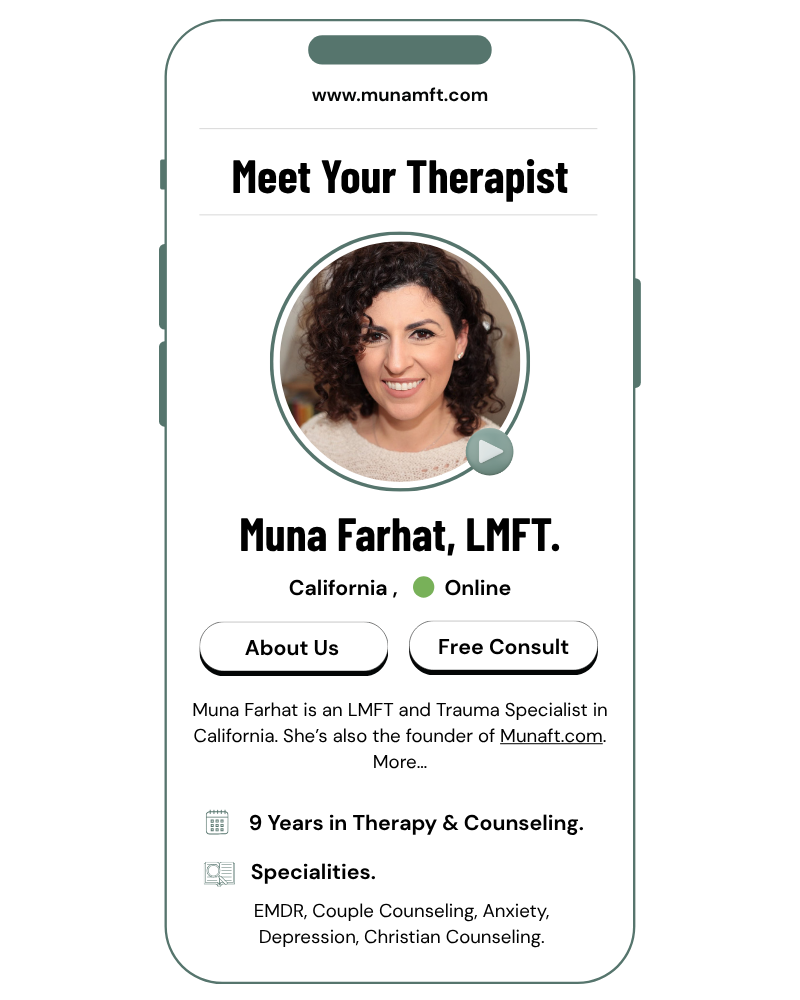
Muna Farhat, LMFT is a Licensed Marriage and Family Therapist based in San Jose, CA.
She holds the necessary credentials to practice therapy in California, with expertise in supporting individuals, couples, and families through various emotional and relational challenges.
As a Licensed Marriage and Family Therapist, Muna adheres to strict confidentiality standards outlined by California state law and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Your personal information is securely stored and only shared with your explicit consent, except in legally mandated situations.
Therapy is a collaborative process where you work with a trained professional, like Muna, to address emotional, mental, or relational challenges. It can help you gain insight, develop coping strategies, and achieve personal growth or resolution of specific issues.
Counseling and therapy are often used interchangeably, but counseling typically focuses on specific issues or short-term goals (e.g., coping with a life transition), while therapy may involve deeper exploration of long-standing patterns. Muna offers both, depending on your needs.